Hernia, in layman's terms, is the organs in the abdominal cavity break out through the natural channels or cracks in the abdominal wall. Hernia in dogs mainly includes umbilical hernia, scrotal hernia, perineal hernia, inguinal hernia, and diaph...
Hernia, in layman's terms, is the organs in the abdominal cavity break out through the natural channels or cracks in the abdominal wall. Hernia in dogs mainly includes umbilical hernia, scrotal hernia, perineal hernia, inguinal hernia, and diaphragmatic hernia. In case of mild hernia, the organ that is released can be pushed back into the abdominal cavity through the hernia hole; in case of severe hernia, it cannot be pushed back into the abdominal cavity because the hernia hole is closed or the organ is adhesion to the surrounding area.

Types of hernia
1. Umbilical hernia: Umbilical hernia refers to the disease caused by the intraperitoneal organs of a dog and the peritoneum entering the subcutaneous part of the umbilical bore through the umbilical bore.
Daily pet knowledge Dogs also have small hernia, how to treat and prevent
2. Scrotal hernia: Scrotal hernia is often found in young dogs and evolved from inguinal hernia. The symptoms are in the inguinal area. You can see or touch the lump, and you will have discomfort symptoms such as bloating in the lower abdomen, bloating, abdominal pain, constipation, poor nutritional absorption function, easy fatigue and physical decline.
3. Perineal hernia: Perineal hernia refers to the recessed connective tissue after the peritoneum and abdominal organs pass through the pelvic cavity and break out into the subcutaneous skin of the perineum. This disease is a common disease in elderly dogs, and it usually occurs in male dogs over 6 years old who have not undergone surgery.
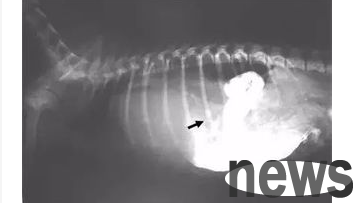
4. Inguinal hernia: The inguinal area is a triangular area located at the junction of the lower abdominal wall and the thigh. Inguinal hernia refers to the hernia formed by the abdominal internal organ protruding to the surface through the defect in the inguinal area, commonly known as "hernia". According to the relationship between the hernia ring and the inferior abdominal wall artery, inguinal hernia is divided into two types: inguinal oblique hernia and direct inguinal hernia. Inguinal hernia can be congenital and acquired.