In recent years, the incidence of pet skin diseases has increased significantly, and has become a common problem in about one-third of clinical cases. Although this type of disease does not usually directly threaten the life of a pet, its treatment...
In recent years, the incidence of pet skin diseases has increased significantly, and has become a common problem in about one-third of clinical cases. Although this type of disease does not usually directly threaten the life of a pet, its treatment process is often long and complex, and it is prone to recurrence, especially stubborn skin diseases, which often put pet owners in the dilemma of difficult treatment and difficulty in completely curing.
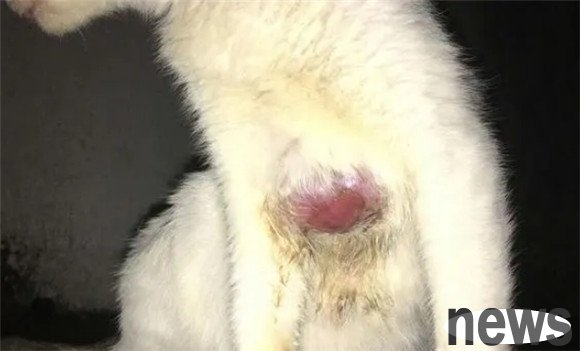
1. Parasitic skin diseases
·Skin diseases caused by scabies mites are extremely contagious. The insect body mainly parasitizes in areas with thin skin and thin hair, such as the lateral ear tip, ear root, toes, eyes and mouth. In severe cases, it can spread throughout the body. Yin tides in the living environment or exposure to various stimuli will aggravate the development of the disease.
·Skin diseases caused by ear itchy mites:
are mainly parasitized in the ear canal and are transmitted through contact.
·Skin diseases caused by demodex:
Parasitizes in dogs' hair follicles and sebaceous glands, and systemic demodex disease is often caused by decreased immune function.
·Skin diseases caused by fleas and lice:
Fleas and lice invade skin tissue, causing skin itching.
2. Fungal skin disease
Fungal skin disease is caused by fungal infection, with the most common pathogens of M. canis, followed by M. gypsum-like, which is the most common skin disease in dogs.
3. Bacterial skin diseases
This type of skin diseases are mostly pyoderma and interphalangeal pyoderma caused by suppurative bacterial infections such as Staphylococcus. Pusts occur between the toes of the single or four limbs of the dog, forming a fistula.

4. Complex reactivity include food, medicine, chemicals, environmental factors, hereditary, hormone abnormalities and allergic qualities.
·For example, eczema
is a mild allergic inflammation of the skin. Acute eczema is characterized by a rash with a punctate or polymorphic boundary that is not obvious with itching and mossy-like changes in the skin and wrinkles, accompanied by pigmentation.